AI can revolutionize enterprise design systems by automating repetitive tasks, improving design consistency, and bridging gaps between design and development. Here’s how to get started:
- Set Goals and Assess Readiness: Identify challenges like reducing manual work or improving team alignment. Ensure your design system is well-structured and machine-readable.
- Plan Resources: Evaluate tool compatibility, infrastructure, and budget. Prepare for costs like subscriptions, training, and long-term maintenance.
- Build Prototypes: Use AI tools to create functional components. Test for accuracy and efficiency while collecting team feedback.
- Deploy AI: Standardize your system with clear rules, metadata, and APIs. Tailor AI outputs to match your brand and security needs.
- Test and Scale: Validate AI-generated components, measure performance, and gradually roll out across teams with proper training and version control.
AI tools like UXPin Merge can create code-backed components, saving time and reducing errors. For example, Atlassian achieved a 70% accuracy rate in UI replication and improved team confidence by 85%. By following these steps, you can streamline workflows and maintain consistency as your organization grows.
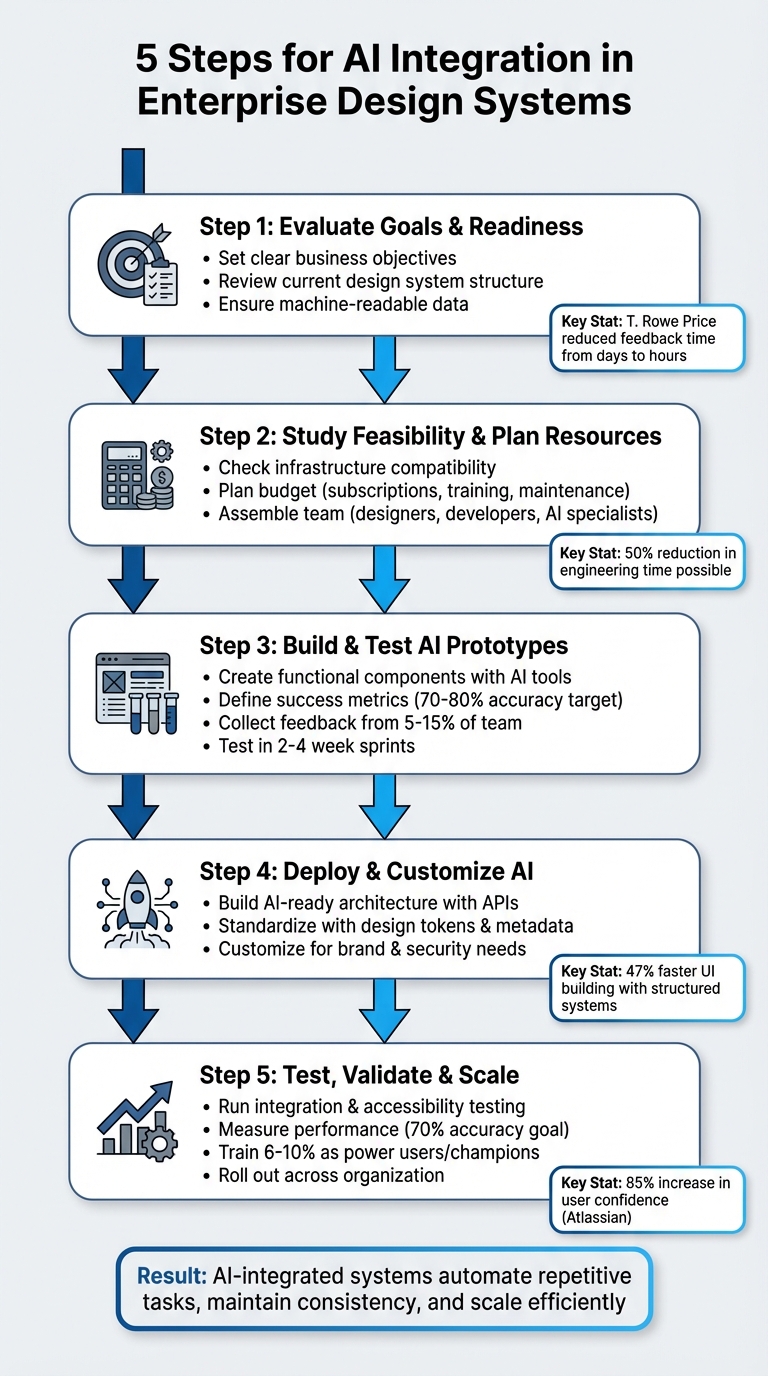
5-Step Process for AI Integration in Enterprise Design Systems
Step 1: Evaluate Your Goals and Design System Readiness
Set Clear Business Objectives
Start by identifying the specific challenges your business is trying to address. Are you aiming to cut down on manual tasks? Accelerate workflows? Ensure design consistency across teams? Each of these goals may require a different AI strategy.
Take T. Rowe Price as an example. Under the guidance of Sr. UX Team Lead Mark Figueiredo, the company adopted code-backed prototyping to address delays in feedback loops. This change reduced feedback time from days to just hours, ultimately saving months on their project timelines.
Your goals should directly tie to measurable results. For instance, if faster time-to-market is your priority, AI can help by generating code-backed UI components from text prompts. If reducing costs is your focus, implementing code-backed design systems could cut engineering hours by up to 50%. These efficiencies can lead to substantial savings, especially when managing large teams of designers and engineers.
Once your objectives are clear, the next step is to evaluate whether your current design system is ready to support AI integration.
Review Your Current Design System
AI thrives on structured, machine-readable data. Before diving into AI integration, take a close look at your design system’s structure, naming conventions, and documentation quality. A well-organized system minimizes errors and maximizes AI’s potential.
Start with a UI inventory. Catalog all reusable components, colors, text styles, and patterns to pinpoint inconsistencies. AI tools often struggle with poorly organized systems – for example, when button variants have inconsistent names or when design tokens don’t align between design files and production code. Diana Wolosin, author of Building AI-Driven Design Systems, emphasizes:
“Design systems must evolve into structured data to be useful in machine learning workflows”.
A great example of preparation comes from Atlassian’s Design System team. In November 2025, under the leadership of Lead Design Technologist Lewis-Ethan Healey, they created 2,000 lines of custom instructions and converted their top-navigation options into JSON. This hybrid approach of templates and structured data enabled AI to replicate their design standards with about 70% accuracy in one attempt. Without such groundwork, AI might produce errors like referencing non-existent APIs or component names.
To make your system machine-readable, ensure each component includes metadata, such as props, states, variant logic, accessibility tags, and usage rationale. Additionally, review your documentation format. Modular, “atomic documentation” – small, context-rich units tied directly to components – works far better for AI than lengthy, monolithic guides.
AI that knows (and uses) your design system
Step 2: Study Feasibility and Plan Your Resources
Once your objectives are clear and your design system is in place, it’s time to assess your infrastructure and map out the resources needed for integrating AI effectively.
Check Infrastructure and Tool Compatibility
Before diving in, make sure your technical setup can handle AI integration. The foundation for success lies in three key areas: a unified data structure, API-first connectivity for real-time AI interactions, and a modular architecture built on microservices.
Select design tools that support code-backed components and AI-driven features. For instance, UXPin pairs well with React component libraries and offers AI-powered component creation through its Merge feature. Your team should also be comfortable working with tools like VSCode, Node.js, and frameworks such as React, JSX, and CSS libraries like Tailwind or MUI.
Plan Your Budget and Resources
Budgeting for AI integration involves more than just tool subscriptions. Factor in platform fees, API costs, staffing, training, and long-term maintenance.
For example, UXPin Merge and its AI Component Creator require subscriptions and API keys, which come with usage-based costs. You’ll also need to invest in a diverse team of designers, front-end developers, and AI specialists. Additionally, allocate time for training on topics like component-based design, design tokens, and setting up the development environment.
Organizations relying on separate design and code libraries should prepare for higher maintenance expenses, though full AI-code integration can significantly reduce these costs. Larry Sawyer, Lead UX Designer, highlighted this efficiency:
“When I used UXPin Merge, our engineering time was reduced by around 50%. Imagine how much money that saves across an enterprise-level organization with dozens of designers and hundreds of engineers”.
Start small with a pilot project. Conduct an audit of your UI to pinpoint components that could benefit from AI automation. Define your design tokens early to ensure consistent branding throughout the process.
Step 3: Build and Test AI Prototypes
This is where your planning takes shape. By building prototypes, you can bring AI concepts to life, test their functionality, and refine them for real-world application.
Create Prototypes with AI Features
Start by building prototypes that highlight AI capabilities aligned with your business goals. Use tools like UXPin’s AI Component Creator combined with React libraries such as MUI or Tailwind to create functional components. These prototypes should mimic real-world scenarios, not just serve as proof-of-concept models.
Focus on components that offer the most value when automated by AI – think buttons, forms, cards, or navigation elements. Generate multiple variations of these components, ensuring they adhere to your design tokens and branding guidelines. This process helps you evaluate how well AI-generated elements align with your design language and where manual adjustments might be needed. It’s worth noting that 25% of all new code is currently AI-generated, so your prototypes should explore how this trend could enhance efficiency in your workflow.
Define Success Metrics
Once your prototypes are ready, it’s time to measure their effectiveness.
Establish clear metrics to evaluate both the quality of AI-generated outputs and the overall impact on team efficiency. For quality, aim for 70–80% component accuracy on the first generation. This means the components created by AI should closely match your design system standards with minimal rework.
On the productivity side, benchmark your current design timelines over a four-week period. Then, set measurable goals like reducing design time by 40–60%, speeding up component creation by 75–85%, and cutting iteration cycles from 5–6 rounds to just 2–3 rounds. These benchmarks will help you determine whether integrating AI truly streamlines your processes.
Collect Stakeholder Feedback
Feedback is crucial for refining your prototypes and improving your AI integration.
Test your prototypes with 5–15% of your team, ensuring a mix of skill levels and roles rather than only involving advanced users. This diverse group will help uncover usability issues across different workflows. Gather input from designers on component quality and ease of customization, developers on code accuracy and integration, and business stakeholders on strategic alignment.
Conduct evaluations in 2–4 week sprints. Given how quickly AI technology evolves, shorter feedback cycles allow for faster adjustments. Use tools like Airtable, Google Analytics, or Mixpanel to track usage patterns, completion times, and accuracy rates. Document what’s working, what isn’t, and where manual intervention is still required. These insights will guide your deployment strategy in the next phase.
sbb-itb-f6354c6
Step 4: Deploy and Customize AI Integration
Integrating AI into your design system’s infrastructure is the next step to transform your prototypes into scalable, production-ready tools. After validating your prototypes, it’s time to embed these AI solutions into your enterprise environment.
Build an AI-Ready Architecture
For AI to work seamlessly with your design system, it needs structured, machine-readable data – not just visual libraries. This shift allows AI to better understand and interact with your system, enabling smoother machine learning workflows.
Start by creating a consistent framework with naming conventions, design tokens, and component behaviors that machines can easily interpret. Make these elements accessible through API endpoints. Your architecture should provide design tokens, component structures, and documentation via APIs or through the Model Context Protocol (MCP). MCP, a growing standard, allows AI agents to query your system directly instead of relying on static style guides.
This structured foundation builds upon earlier efforts to standardize design tokens and metadata. Each component should include detailed metadata that outlines design intent, such as states, props, accessibility requirements, and platform constraints. This level of detail helps minimize AI errors and confusion. As Pierre Bremell explains:
“If the structure of your system is not consistent and machine-readable, tools like Cursor will fail to understand it”.
The benefits of this approach are clear. For instance, developers working with structured systems like IBM’s Carbon Design System reported building UIs 47% faster compared to starting from scratch – even without AI assistance.
Adapt AI for Enterprise Needs
Once your architecture is AI-ready, the next step is to tailor the AI outputs to align with your enterprise’s unique brand and security requirements.
Generic AI outputs won’t meet the demands of enterprise-scale operations. Customize AI-generated components to adhere to your organization’s branding, design standards, and security protocols. Using open-source libraries such as MUI, Ant Design, or Tailwind can provide a solid starting point, ensuring the generated code follows industry practices.
Ensure AI generates components using your predefined enterprise themes instead of generic inline CSS. This approach maintains brand consistency across thousands of components and prevents style inconsistencies. Align design tokens across tools and production code to eliminate mismatches between AI outputs and your system.
Additionally, prioritize AI tools that avoid using your proprietary design data to train external models. To safeguard your system, implement version control and access management workflows. Use linting and anomaly detection tools to catch and address inconsistencies early, preventing them from spreading across your organization.
Step 5: Test, Validate, and Scale Your AI System
Once your AI-ready architecture is deployed, the next step is to thoroughly test and strategically scale your system. This ensures the AI integration operates smoothly and consistently across your organization before rolling it out fully.
Run Integration and User Testing
Testing AI features goes far beyond just checking if they work. Your testing process should include visual regression tests to catch unexpected layout changes, behavioral analysis to see how components react to user interactions, performance profiling to measure load times, and accessibility testing to ensure compliance with WCAG standards.
Incorporate these AI-driven tests directly into your CI/CD pipelines. This way, low-quality components can be flagged and blocked automatically with each code commit. Make sure to validate components across major browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge to guarantee consistent rendering.
While AI can handle repetitive testing tasks efficiently, human oversight is still essential. Teams should review AI outputs, refine them as needed, and conduct regular fairness audits to ensure inclusivity in AI-generated components. Assign dedicated accessibility champions to oversee compliance and proper labeling. Once testing confirms that everything functions as expected, it’s time to measure performance and fine-tune the system.
Measure Performance and Iterate
Evaluate your AI tool’s performance against predefined metrics. Aim for around 70% design system accuracy on the first pass. To push accuracy higher, shift from open-ended prompts to structured JSON configurations. This approach can drastically reduce errors like logo misplacements or navigation inconsistencies.
Using hybrid templates – pre-coded components combined with AI-generated instructions – can also help minimize errors and improve output quality. Monitor how quickly your teams can create interfaces with AI assistance compared to manual methods, and assess the consistency of the generated components. If the results don’t meet your expectations, adjust configurations or provide additional training data to enhance accuracy. These performance insights will guide you in refining your system before scaling it across the organization.
Roll Out AI Across Your Organization
Scaling AI effectively requires careful planning and solid change management. A well-executed rollout can significantly boost confidence in AI tools. For instance, one initiative led to the creation of production-ready prototypes aligned with design systems, and 85% of participants reported increased confidence in using AI tools.
To support adoption, establish a champions program by training 6% to 10% of your users as power users. These individuals can offer one-on-one training sessions and host office hours to help their colleagues become comfortable with the tools. Set up granular permissions to control who can view and edit the design system, ensuring a single source of truth during the rollout. Use version control to track component changes, manage themes, and coordinate updates across products. Allow teams to develop new components for emerging use cases and contribute them back to the central library through version-controlled releases. This collaborative approach ensures your AI system continues to evolve and meet organizational needs.
Benefits of AI-Integrated Design Systems
Integrating AI into enterprise design systems isn’t just a trend – it’s a game-changer for efficiency, teamwork, and scalability. By weaving AI into the process, organizations are cutting down prototyping time from hours (or even days) to mere minutes. This speed boost allows teams to test and refine ideas faster than ever, keeping projects on track and innovation flowing.
AI also steps in to handle repetitive tasks that typically eat up valuable time. Think resizing components, generating design variants, or updating documentation – AI takes care of these so your team doesn’t have to. This automation addresses what’s often called the “Maintenance Paradox”, where the effort to maintain a system grows faster than the team’s ability to keep up. With AI, this workload becomes manageable, freeing up your team to focus on more strategic, creative work.
Another big win? AI creates a shared, machine-readable language between designers and developers. It keeps an eye on design changes and updates the codebase automatically, eliminating the need for manual handoffs. As Vishwas Gopinath from Builder.io puts it:
“The design system team’s job becomes more strategic. Instead of pushing updates through the pipeline, they define the language of the product while AI handles the housekeeping”.
AI-powered systems also grow with your organization. Unlike traditional systems, which can spiral into “design entropy” as new team members join, AI-integrated systems maintain order through standardized rules that machines can read and enforce. For example, Atlassian’s use of AI not only boosted user confidence but also made design system expertise more accessible across the company.
Before and After: Design Systems with AI
Here’s a snapshot of how AI transforms traditional design systems:
| Metric/Feature | Traditional Design System | AI-Integrated Design System |
|---|---|---|
| Documentation | Often outdated; relies on manual updates | Automatically updated with AI-generated stories and examples |
| Prototyping Speed | Takes hours or days for high-fidelity flows | Achieved in minutes using visual inputs |
| Consistency | Suffers from “design drift” as variants multiply | AI enforces design tokens and architectural rules |
| Handoff Process | Requires manual interpretation of static assets | Seamless, automated code handoffs |
| Maintenance Effort | Grows faster than team capacity | AI identifies redundancies and handles routine tasks |
| Scalability | Becomes chaotic with new hires (“design entropy”) | Scales efficiently with machine-readable rules |
AI-integrated design systems don’t just improve workflows – they redefine how teams collaborate, adapt, and grow. By automating the tedious parts and standardizing processes, AI allows design teams to focus on what they do best: creating meaningful, impactful designs.
Conclusion
Bringing AI into enterprise design systems calls for careful planning, thorough testing, and thoughtful scaling. This guide outlines five key steps to follow: begin by assessing your goals and the readiness of your system, then study feasibility and allocate resources. Next, focus on building and testing AI prototypes, deploy them with necessary customizations, and finally, validate and scale across your organization. Each phase builds on the previous one, ensuring AI integration is not only functional but also efficient and effective. These steps can lead to real gains in design consistency and operational efficiency.
For example, in November 2025, Atlassian reported a 70% accuracy rate in UI replication and an 85% increase in participant confidence after training nearly 1,000 product designers and managers.
However, without proper standards and execution, “design entropy” can take over – resulting in inconsistent patterns and overwhelming maintenance. AI acts as a safeguard against this chaos, enforcing rules, automating updates, and ensuring alignment across teams.
UXPin offers tools to simplify this process, combining code-backed prototyping with AI-driven design features. Its Merge AI functionality allows teams to work directly with real React components, producing prototypes that are ready for production. This approach eliminates manual handoffs and ensures your design system remains consistent as it scales.
FAQs
How does AI improve design consistency in enterprise design systems?
AI plays a key role in maintaining design consistency by serving as a virtual safety net for enterprise design systems. It works behind the scenes to automatically check components for correct token usage, proper naming conventions, and adherence to spacing rules. When it spots an issue, it flags it immediately and offers suggestions for fixes, cutting down on the manual work needed to keep everything consistent in large-scale projects.
Beyond that, AI can organize design guidelines into searchable knowledge bases, making it simple for teams to locate the right components or patterns when they need them. It can even generate UI elements that align perfectly with brand standards – covering colors, typography, and spacing – so every design stays true to the brand identity. These features allow enterprises to scale their efforts efficiently while delivering a seamless and unified user experience.
What should I focus on when preparing a design system for AI integration?
To get your design system ready for AI integration, start by focusing on clear governance and organized data management. Stick to consistent versioning methods, like semantic versioning, and keep detailed changelogs. This helps AI tools stay updated and interpret changes accurately. Standardizing naming conventions, token structures, and component behaviors is key to ensuring that AI can effectively work with your design system.
Make sure your design system is built to scale and AI-compatible by adopting flexible, data-driven workflows. Automate repetitive tasks, such as quality assurance, accessibility checks, and even code generation, to save time and improve efficiency. Leverage tools that support code-backed components and offer AI-powered features like automated backups and rollback options to simplify the process. Lastly, bring your teams together with shared objectives and establish clear metrics to track the success of AI implementation as your design system grows.
How can businesses evaluate the success of integrating AI into their design systems?
To gauge how well AI contributes to design systems, organizations should rely on measurable, actionable metrics that highlight improvements in efficiency and return on investment (ROI). Here are a few key areas to focus on:
- Time-to-market: Track how quickly new UI features are launched before and after implementing AI. Many teams have reported cutting delivery times by 30–50%, which can make a huge difference in fast-paced industries.
- Cost savings: Estimate the developer hours saved by using AI-generated components, then translate those hours into dollar amounts based on your team’s average hourly rate.
- System stability: Keep an eye on metrics like the success of AI-driven versioning, the frequency of rollbacks, and quality assurance (QA) pass rates. A system with fewer rollbacks and higher QA success rates reflects greater reliability.
Additionally, gathering feedback from team members on aspects like speed, accuracy, and ease of use can provide deeper insights. Tools such as UXPin make this process easier by offering features to track component reuse, manage version control, and automate workflows. By consistently reviewing these metrics, businesses can clearly see how AI impacts efficiency, reduces costs, and strengthens the overall design system.

