Double Diamond Design Process – The Best Framework for a Successful Product Design
The Double Diamond design process is a widely used methodology for identifying a problem and developing a solution. This outcomes-based framework encourages creativity and innovation while focusing on the core issue and its impact on end-users.
It was introduced by the British Council so that designers could follow a standardized design process and make that process super clear, with visual representation that outlines distinct phases: Discover, Define, Develop, and Deliver.
Deliver better products to your users with the world’s most advanced prototyping tool. Sign up for a free trial to explore interactive prototyping with UXPin. Try UXPin for free.
What is the Double Diamond?
The Double Diamond model is a framework for innovation and design developed by the British Design Council in 2005. The Design Council wanted a simple design process for delivering projects, no matter the methods and tools used.
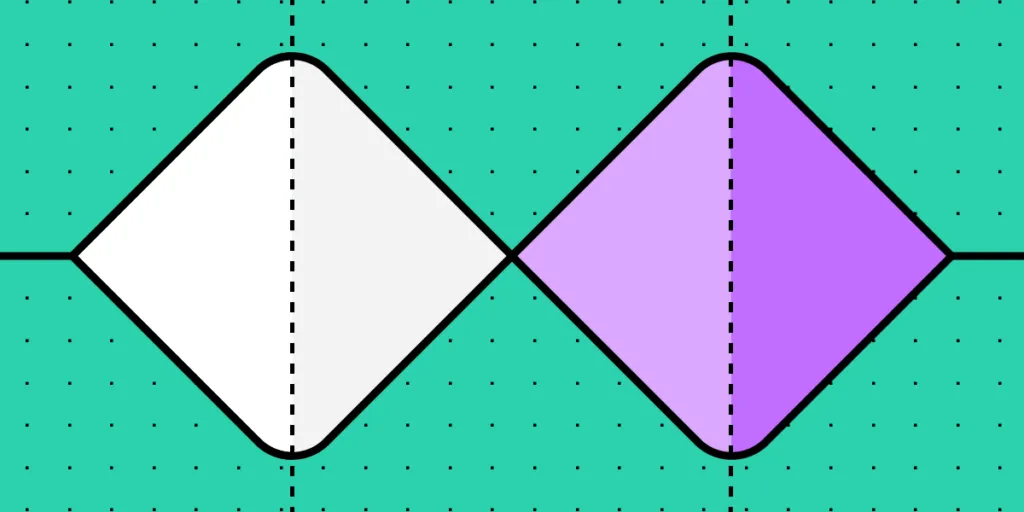
The design framework features two diamonds:
- a diamond that represents the problem.
- a diamond that stands for the solution.
Designers work within these two diamonds. They help them to truly understand the problem and thoroughly test their solutions.
Once designers identify a core issue in the first diamond, they create a design brief as a foundation for the second. The second diamond focuses on prototyping and testing a solution until its ready for release.
Why Are There Diamonds in this Process?
The Double Diamond design model was developed as a response to the need for a standardized design process description that could be universally applied across various design disciplines. Before its introduction, there was a lack of a cohesive framework that could describe the entire design process from start to finish, which led to inconsistencies and inefficiencies in design practices.
The Double Diamond we know as a design framework came from the British Design Council, but the inspiration for this process came from Hungarian-American linguist Béla H. Bánáthy’s divergence-convergence model.
Béla’s model looks very similar to the design framework where he used the first diamond to explore an issue widely and deeply (divergent thinking) and then took an appropriate focused action (convergent thinking.)
Diamond One – Discovering and Defining the Problem
The first diamond is about UX research and exploration, often referred to as the “problem space”–similar to the empathize and define stages of the design thinking process.
Designers start by researching the problem and user needs. This phase might include reviewing analytics and UX artifacts, interviewing end-users, conducting a service safari, and other early-phase research methods.
In phase two, designers use discovery phase research to define the problem and how it impacts users. Design teams may iterate over phases one and two a few times until they get to the core issue. Next, they synthetize all the insights together.
At the end of phase two, designers create a design brief to guide the second half of the design process towards finding an appropriate solution.
Diamond Two – Developing and Delivering the Solution
The second diamond is about ideating, prototyping, and testing to find a suitable solution.
The develop phase is a busy stage of the Double Diamond framework where teams use various tools and methods, including:
- Workshops and brainstorming: gathering as a team to ideate, hypothesize, conduct experiments, and discuss possible solutions.
- Low-fidelity design: sketches, wireframes, paper prototypes, and other lo-fi methods designers use to develop and test many ideas quickly.
- Cross-functional collaboration: designers meet with engineers, product owners, and other stakeholders to discuss ideas for feedback on possible challenges and constraints.
The development phase is an iterable process of ideation, prototyping, and testing several ideas until designers identify a single solution with the most potential to:
- Solve the problem
- Align with user needs
- Meet budget and technical constraints
In some circumstances, designers choose a single solution or select their best two or three ideas for high-fidelity prototyping and testing in the deliver phase. The first goal is to eliminate those that don’t work until you arrive at a single solution.

Once designers arrive at a single solution, they conduct further testing to refine the final prototype. During this round of testing, designers focus on usability and user experience to ensure the final result satisfies the design brief and stakeholders.
If designers encounter a problem, they return to the develop phase to find a solution, iterating and testing until they find a solution.
Once prototyping and testing are complete, design teams prepare for the design handoff, including documentation, annotations, assets, and other instructions engineers will use to develop the final product for release.
Lastly, design teams must conduct a UX audit and quality assurance to ensure the final release meets the project’s requirements, business goals, and user needs.
Who follows Double Diamond Design Framework?
The Double Diamond design framework is widely adopted by various organizations and professionals across different industries.
- IDEO: As a pioneer in design thinking, IDEO incorporates the Double Diamond framework to structure its innovation processes. Tim Brown, co-chair at IDEO, has often highlighted the framework’s value in understanding problems before jumping to solutions.
- Design Council: The British Design Council, which developed the Double Diamond model, extensively uses and promotes this framework as a standard for best practices in design.
- Google: Google’s design sprints and product development processes often reflect the principles of the Double Diamond, focusing on deep problem understanding and iterative solution development.
- Microsoft: Microsoft integrates the Double Diamond framework in its user experience and product design processes, particularly in teams focused on user-centered design and innovation.
- University Design Programs: Many university programs, such as those at Stanford’s d.school and the Royal College of Art, teach the Double Diamond framework as part of their design thinking and innovation curricula. It provides students with a structured approach to tackling complex design challenges.
- Charities and NGOs: Organizations like the Red Cross and UNICEF use the Double Diamond framework to design and implement programs that effectively address the needs of the communities they serve, ensuring a deep understanding of problems.
4 Phases of the Double Diamond Design Process
The Double Diamond design process comprises two diamonds and four phases (also called the four Ds):
- Discover
- Define
- Develop
- Deliver
Discover
Objective: To understand the problem space thoroughly by gathering insights and exploring the broader context of the design challenge.
- Activities: This phase involves extensive research, both qualitative and quantitative. Techniques include desk research, field studies, user interviews, focus groups, and observations. The goal is to gather as much relevant information as possible about the problem, the users, and the context in which the problem exists.
- Outcome: A deep understanding of the problem space, including user needs, pain points, and opportunities for innovation. This phase aims to challenge assumptions and uncover insights that will inform the next phase.
Define
Objective: To synthesize the insights gathered during the Discover phase into a clear and actionable problem statement.
- Activities: In this phase, designers analyze and organize the data collected. Techniques such as affinity diagrams, root-cause analysis, and the “5 Whys” method are used to identify the core issues and refine the problem definition. Design synthesis helps in distilling complex information into clear insights.
- Outcome: A well-defined problem statement or design brief that provides a focused direction for developing solutions. This phase sets the stage for ideation and prototyping by clearly articulating what needs to be addressed.
Develop
Objective: To ideate and prototype multiple potential solutions to the defined problem.
- Activities: This phase involves brainstorming, sketching, and creating prototypes. Tools like personas, wireframes, and Minimum Viable Products (MVPs) are used to visualize and test ideas. The development phase encourages divergent thinking, allowing for the exploration of various solutions and approaches.
- Outcome: A range of prototypes or preliminary solutions that can be tested and iterated upon. The goal is to explore different ideas and refine them through feedback and testing, ensuring that the solutions are viable and effective.
Deliver
Objective: To finalize and implement the best solution, and to evaluate its impact.
- Activities: In this phase, the most promising prototypes are refined and developed into final products or solutions. This involves extensive testing, validation, and iteration based on user feedback. Surveys, usability testing, and pilot programs are common methods used to gather final insights before launch.
- Outcome: A polished, user-validated product or solution that addresses the initial problem effectively. The Deliver phase also includes post-launch evaluation and gathering feedback to inform future improvements and iterations.
How to use Double Diamond Design Process
Here’s a practical example of using a double diamon design process in your workflow.
Phase 1: Discover
- User Research: Conduct interviews and surveys with target users.
- Market Research: Study competitors and industry trends.
- Stakeholder Interviews: Gather insights from stakeholders.
- Empathy Mapping: Create empathy maps to understand user emotions and motivations.
Phase 2: Define
- Synthesize Data: Use affinity diagrams to identify patterns.
- Problem Statement: Develop a clear and concise problem statement.
- User Journey Mapping: Map user journeys to pinpoint pain points.
- Design Brief: Draft a brief outlining project goals and constraints.
Phase 3: Develop
- Ideation: Brainstorm solutions through collaborative workshops.
- Prototyping: Create wireframes and sketches.
- User Testing: Test prototypes with real users.
- Iteration: Refine designs based on feedback.
Phase 4: Deliver
- High-Fidelity Prototypes: Finalize design details in high-fidelity mockups.
- Development: Build the site with close collaboration between designers and developers.
- Quality Assurance: Conduct extensive testing.
- Launch and Monitor: Launch the site and continuously monitor performance for further improvements.
By following the double diamond design process, you ensure a thorough and user-centered approach to designing a new site, maximizing the chances of its success by deeply understanding user needs, exploring and refining solutions, and effectively implementing and launching the final product.
Try End-to-End UX Design With UXPin
Prototyping and testing are significant in the end-to-end design process, including the Double Diamond framework. Designers must use high-quality prototypes to thoroughly test potential solutions and achieve accurate results.
Unfortunately, high-fidelity prototyping can be slow with certain tools, which isn’t ideal when testing many ideas in the Double Diamond design process.
With fully interactive design from UXPin, designers don’t have to compromise on quality for speed. They can build high-fidelity prototypes that look and function like the final product. Better prototypes yield accurate results during testing, allowing designers to go beyond what’s possible with image-based design tools.
UXPin also comes standard with built-in design libraries, allowing design teams to drag and drop components to build high-fidelity mockups in minutes. In a few clicks, they can add Interactions to create prototypes with code-like functionality, including:
- States: create multiple states for any element, each with separate properties and interactions.
- Variables: capture user inputs and take action based on the data to create dynamic, personalized user experiences during testing.
- Conditional Interactions: create “if-then” and “if-else” rules to execute different reactions to user actions and inputs.
- Expressions: design functions to perform complex operations traditionally only available with code, including form validation, computational components, simulate password authentication, and more.
No matter the framework, UXPin can enhance your design process to create better user experiences for your customers. Sign up for a free trial and discover the possibilities of code-based design with UXPin.